ROSEBANK


| Distillery Opened | Capacity | Malting Floor | Washback Type | Number of Washbacks | Number of Wash Stills | Number of Spirit Stills |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1840 | / | / | / | / | 1 | 2 |
There are records of a family called Stark distilling beside Forth & Clyde, the waterway which linked Scotland's east and west coasts, therefore Glasgow and Edinburgh, as early as 1798.
In 1817, a distillery named Rosebank was operational for two years,
On the opposite bank of the canal, in 1827, the Stark family started running the Camelon distillery.
In 1840, what had been Camelon's maltings were converted by James Rankine into the new Rosebank Distillery.
The Camelon distillery buildings were demolished in 1861, and a new maltings supplying Rosebank was built, with the malt being barrowed over the canal to the distillery on a bridge.
In 1914, the Scottish Malt Distillers (SMD) was founded, and Rosebank Distillery was one of the founding members. In 1925, SMD was folded into Distillers Company Limited (DCL).
Rosebank Distillery ran continuously, except for an interruption during the war, until was mothballed in 1993, when there were only two working malt distilleries left in the Lowlands - Glenkinchie and Auchentoshan. The reason was that the Rosebank owners didn't want to bear the refurbishment costs.
The whisky from Rosebank has always had a great amount of supporters, was often described as the "King of the Lowlands", and there was a glimmer of hope that a new company would start up the distillery again. At the beginning of 2009 though, most of the Rosebank Distillery's equipment was stolen. The buildings were still intact and most of them have been turned into restaurants, offices and flats.
In 2017, Ian Macleod Distillers bought Rosebank Distillery, and now the painstaking process of restoring and reopening the distillery has begun.
- 1798 There are the first traces of distilling in the Forth & Clyde area therefore Glasgow and Edinburgh
- 1817 A distillery called Rosebank becomes operational
- 1840 Rosebank is built by James Rankine on the site of the old Camelon distillery maltings
- 1914 The Rosebank Distillery becomes a founding member of Scottish Malt Distilleries
- 1925 Rosebank forms part of DCL
- 1988 An 8-year-old expression is launched
- 1993 The Rosebank Distillery is closed due to the cost of refurbishment
- 2002 The site is sold to British Waterways
- 2009 Most of Rosebank Distillery's equipment was stolen
- 2017 Ian Macleod Distillers reveals plans to purchase the site and reopen Rosebank Distillery
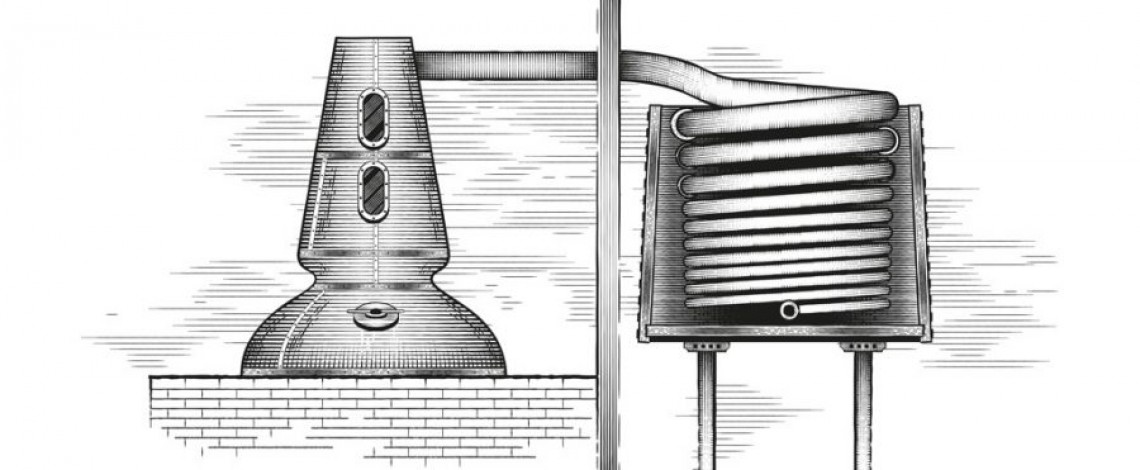
The Rosebank Distillery had a unique production technique of marrying worm tub condensers and triple distillation. This traditional Lowland method of triple-distillation was used at Rosebank Distillery - as opposed to the double distillation method that is used almost everywhere in Scotland.
There was 1 wash still and 2 spirit stills in the Rosebank Distillery's equipment, an unusual configuration.
Most of Rosebank Distillery's equipment, exactly the original stills and mash tun, were stolen during the Christmas and New Year holiday of 2008/2009.
The Rosebank Distillery core products consist of:
- 12 yo Flora & Fauna
- 21 yo Special Release
Image source: Official Rosebank Distillery Website















